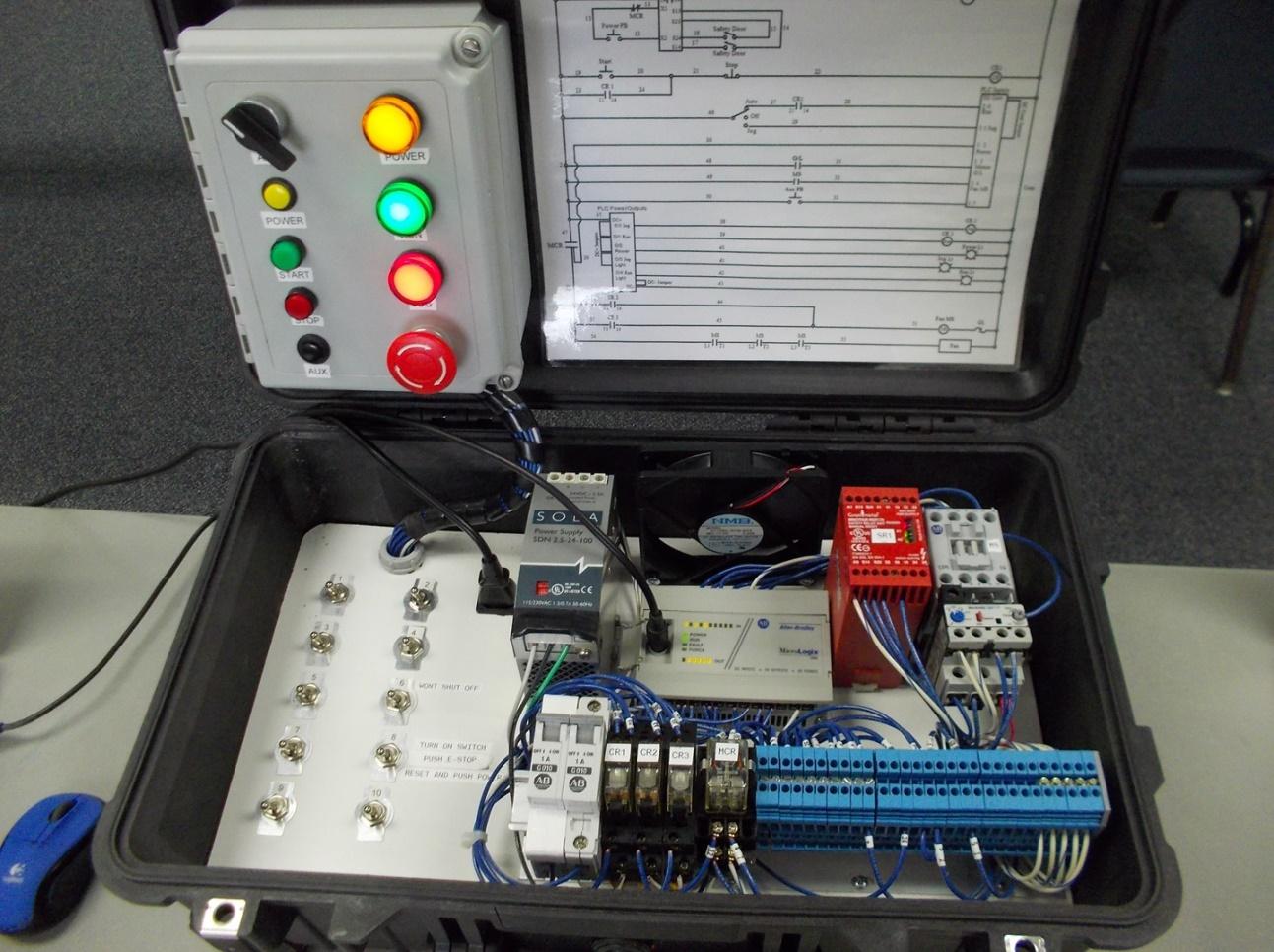
Programmable Logic Controllers or PLC can use a variety of programming languages, but in 99% of the cases, they use Ladder Logic. The main function of these programs is for industrial applications and processes certain machines have to do. It may seem that it is hard to learn like most of the languages, but this is the easiest to learn. You should put more effort into tasks than just learning, but there are some basics that you need to know always.
Thing like the ladder diagram and the parts of PLCs are basics in getting to know this industry. Because it isn’t as available as programs like Python, learning ladder Logic can be done online, and having a mentor will help when you try doing tasks. If you have a controller, it will be much easier to overcome it. There are certifications you can get, but usually, they are expensive, and we live in a world where you just have to prove you have the knowledge to get a job.

Definition of Ladder Diagram
This diagram is a representation of ladder logic PLC programming and relays logic control circuits. They use symbols in order to express the logic behind it. The standard IEC-61131 gave the name to this diagram. This was originally made for electricians, technicians, and electrical engineers so they can make programs that are complex and used for controlling machines without using other programming languages like Fortran, Pascal, and others.
The idea was to have a graphical form of these logical expressions. When you want to use a ladder diagram to present ladder logic it is like you draw a relay control circuit. Because relays were used before and people know how to read them, it is much easier to learn these diagrams. So, the maintenance staff will be able to know what is going on in the system. This means that the troubleshooting PLC problems will be much easier.
Get more information here: https://www.techopedia.com/definition/20292/ladder-logic

Essential Parts of the Diagram
You have to know certain parts of the diagram if you want to be able to draw it. First are the rails and there are two main that you draw as vertical lines. They are going to the end of the page. It is easier to look at them as you would in relays, and they would mean the active and 0-volt connections. The power here flows from left to the right-hand side.
The connection between the rails and logic expression represented as horizontal lines are rungs. A connection between relay components and wires that are connecting the power supply to the switch are rungs in the relay logic circuit. Inputs and outputs also called I/O are actually external control actions and external devices. Inputs can represent a switch or a push button and outputs can be a solenoid valve, electric motor, and similar devices.
To formulate the desired control operations you have to use a combination between logic expressions and inputs and outputs. The descriptions allocated to the addresses are the tag names. The description of the logic expression, input, and output are addressed notations. One of the most important parts are the comments. You can see them at the start of every rung. It is much easier to change it and understand it with comments.
How to Read the Logic?
The most important fact about is that PLC microprocessors like computers operate on a binary system. This means that things can be in one of two situations. To write and read the code ladder logic uses symbolic expressions. For example, a normally open or NO is how we express in the ladder logic something in that is in real-world like a limit switch being activated or a button being pushed.
Because the binary concept says that you have two states like true or false, this means that the NO can be true or false. If it is true it will be represented with green color. Green means that it will move to the next logic expression.
When a switch is turned on the current will flow through the electric circuit. Normally open contact doesn’t mean anything if you don’t have a logic that will decide what action to take. For example, if you are cold you will put your sweater on. So, besides realizing it is cold you also have to make an action after realizing. Cold and sweater on is the binary concept and the logic concept is “then”.
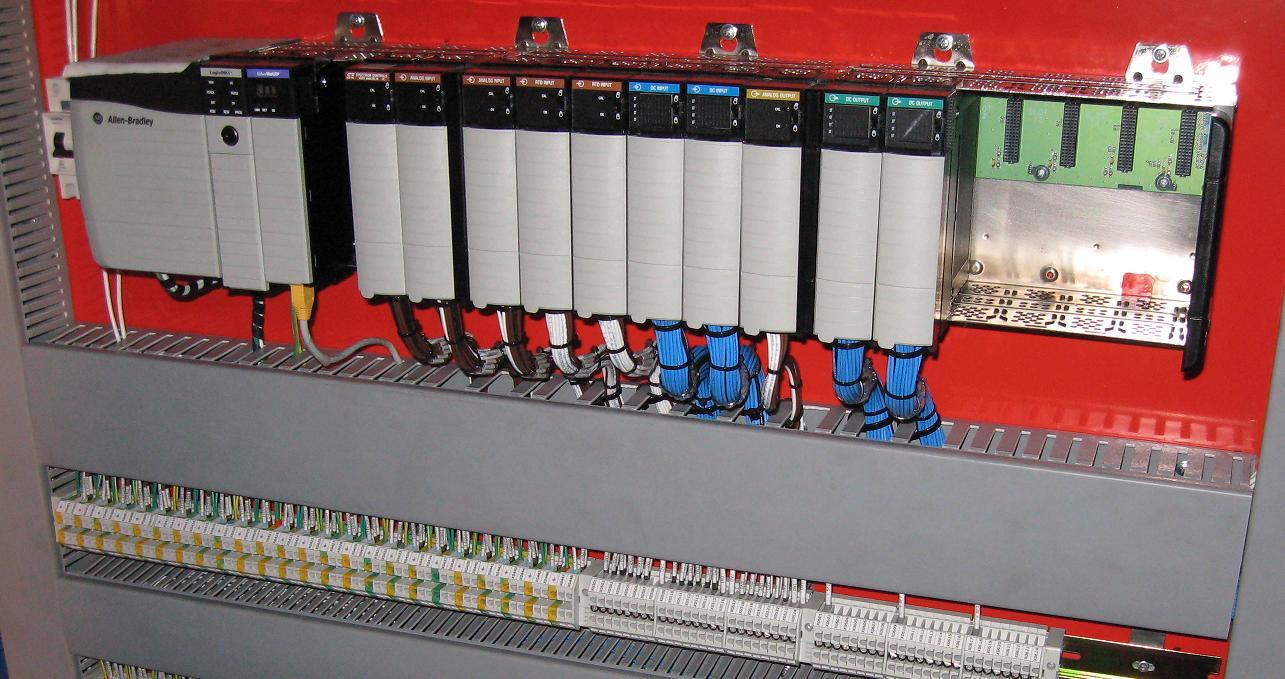
Functions of Ladder Logic
What happens in the real world is a PLC input and for example we will have a normally closed contact named “B”. The result of this function will be named “C”. This will be the output of the controller. When you create these two in the ladder logic you basically have the first line of the code. Of course, you have to insert them into a rung in the diagram.
There is a NOT function which means that the state of an event is opposite as it occurs. The result will be true if the input is false and the other way around. In a logic diagram when you draw this function, it is set as a form of normally closed. The AND function is used when all logics are true. If only one of them isn’t true the result will be false. Click here to read more.
OR Function
This one is a little bit different than the rest. Unlike other, this one doesn’t have the resulting output for multiple PLC inputs. In the ladder diagram, you can use it in a form of a relay coil and two NO contacts. For this function, there will be a branch in the rung. You can look at it as a parallel connection in the electric circuit. This function will examine if only one input is true and the result will be true. If you want the result to be false then all PLC inputs need to be false. When you know this function you are ready to start making your own programs.

I’m Kelly Hood! I blog about tech, how to use it, and what you should know. I love spending time with my family and sharing stories of the day with them.




